Jerusalem Post
ByDR. MAYA ROSMAN
You want the full nutritional value of the vegetables and fruits you eat – but there’s a chance you’re damaging them along the way. Here are some very popular examples.
We all know that cooking changes the nutritional value of food, but is it always necessary to cook? In recent years, more and more people have been adding vegetables, roots and grains to their diet in a natural and fresh form, but it’s not always clear what can be eaten raw, what is better cooked, and what should definitely not be tasted before cooking.
Some foods actually retain health benefits when completely fresh, others offer better absorption after cooking, and some cannot be digested at all without heating.
In this article I collected three particularly common foods: Garlic, beets and oats – what is better raw, what works great both ways, and what may cause stomach pain or toxicity if not cooked?
Here is everything you need to know before taking a bite.
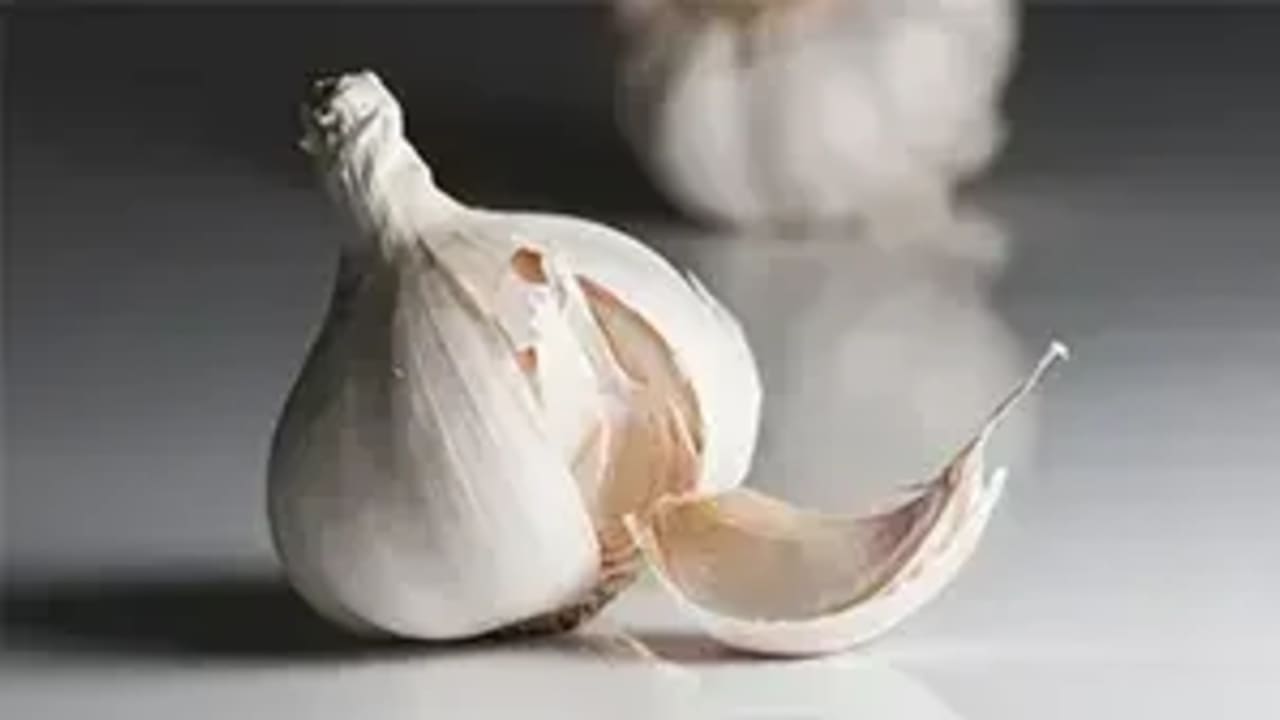
What’s Better – Fresh or Cooked Garlic?
The answer is absolute: Only fresh.
We all already know that garlic is almost like medicine. If we list some of its benefits, we’ll find that it reduces the risk of heart disease, lowers cholesterol, reduces the risk of various cancers, has antibacterial activity, is anti-inflammatory, and reduces blood pressure.
All these good things happen thanks to a substance in garlic called “allicin.” The thing is that this substance begins to form in garlic only after the inner part of the garlic comes into contact with air – meaning after we cut or crush the garlic. During cutting or crushing, the substance begins to form and reaches its highest level after 5–10 minutes.
What happens after that? There is a rapid and significant decrease in the level of the active compound, and according to new research: After one to two hours, almost none of the active compound remains. In such a case, of course, garlic has no health effect. Additionally, and no less important – heating or frying destroys it immediately.
How do we preserve the active compound? By keeping garlic whole until use, freezing is possible, or crushing and waiting 10 minutes for the full creation of the active compound, and only then quickly sautéing / adding at the end of the cooking process.
Is It Allowed to Eat Fresh Beets?
Fresh (raw) beets are completely edible and safe. Both the leaves and the root itself. You can grate them into a salad (like carrots), add them to smoothies, or slice them thinly and soak in lemon juice and vinegar.
Raw beets contain more vitamin C and folic acid compared to cooked beets, but since cooked beets are easier to digest, more iron becomes available to the body. Meaning – both raw and cooked have benefits, and it is possible and recommended to enjoy them both ways.
Is It Allowed to Eat Uncooked Oats?
Yes. The oat flakes we buy in a package, whether fine, thin, thick or “Quaker,” have already undergone a short heating process in the factory, usually gentle steaming. This means that the grain is partially cooked, and therefore the flakes are completely safe to eat even without further cooking.
You can eat them completely dry, such as in yogurt, in an “overnight oats” bowl, in smoothies, and even as a crispy snack after mixing lightly with honey or peanut butter, cocoa and silan.
It is important to emphasize that cooking does slightly change the way the body breaks down the starch: It softens the fibers and allows easier and faster digestion for some people, but there is no significant nutritional advantage. In terms of nutritional values, we’re talking about the same fibers, the same vitamins, and the same heart-beneficial beta-glucan.
A study published in the Journal of Nutrition found that consuming beta-glucan from oats, whether cooked or uncooked, contributes to reducing LDL, improving feelings of fullness, and slowing the rise of blood sugar. Meaning, the health benefits are preserved even when the flakes are not cooked.